The world of computing is on the cusp of another significant transformation. Indeed, relentless innovation in processor design drives this. Crucially, Intel’s ambitious roadmap lies at the heart of this evolution; specifically, it features two pivotal next-generation architectures: Intel Arrow Lake Nova Lake. Thus, these upcoming CPU families are more than incremental updates; instead, they represent a bold strategic play by Intel. Ultimately, the goal is to redefine performance, efficiency, and AI capabilities, especially across desktop and mobile platforms.
Intel isn’t just building chips; rather, they’re crafting a multi-generational strategy. Furthermore, this approach addresses diverse user needs. For example, it serves hardcore gamers and content creators; similarly, it also supports everyday productivity. Moreover, it handles the burgeoning field of AI acceleration. Therefore, understanding Arrow Lake’s distinct advancements, as well as its powerful successor, Nova Lake, offers a clearer picture. Consequently, it shows where your future computing experience is headed.
Intel’s Vision: Redefining Performance and Efficiency
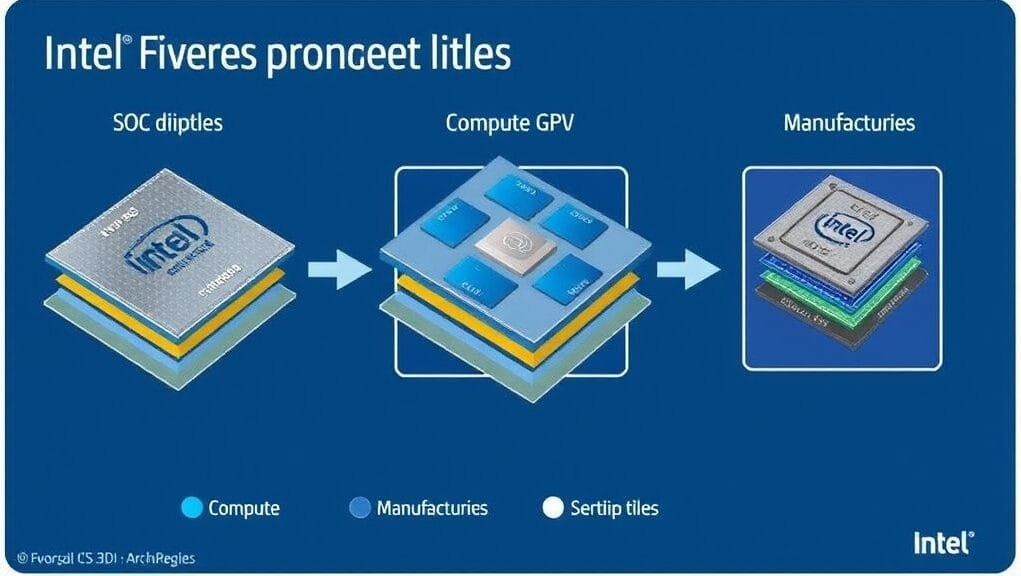
Intel’s journey towards these next-gen processors reflects a deep commitment. This commitment, in fact, is to innovation and regaining market leadership. A disaggregated, chiplet-based design is central to this vision, and it leverages advanced packaging technologies like Foveros. Specifically, this modular approach allows Intel to integrate specialized “tiles.” Furthermore, these tiles perform different functions. Moreover, Intel fabricates each on the most suitable manufacturing node, thereby optimizing performance, power efficiency, and cost.
Furthermore, this strategy delivers more than just raw speed; instead, it encompasses holistic improvements in computing. For instance, Intel integrates powerful AI acceleration directly into the CPU. Additionally, Intel enhances graphics capabilities, and it ensures robust platform features. Ultimately, the evolution from Arrow Lake to Nova Lake showcases Intel’s long-term plan. This plan, moreover, delivers breakthroughs, especially catering to tomorrow’s computing challenges.
Arrow Lake: The Present Foundation of Core Ultra
Significantly, Intel Arrow Lake Nova Lake‘s immediate predecessor recently launched for desktop platforms as the Core Ultra (Series 2) processors. However, Intel expects mobile variants in early 2025. These, consequently, will bring innovations to more devices. Therefore, Arrow Lake signifies a significant departure from monolithic CPU designs; instead, it embraces a sophisticated chiplet architecture.
Furthermore, this design utilizes Intel’s cutting-edge Foveros 3D packaging technology. This technology, consequently, allows stacking different components, or “tiles.” In order to achieve optimal results, Intel optimizes each tile for its specific function, thus leveraging a mix of advanced manufacturing processes.
A Glimpse into Arrow Lake’s Chiplet Design
Arrow Lake’s modular construction is a marvel of modern engineering. To illustrate, consider the intricate assembly of its various tiles:
- The crucial compute tile houses the processor’s main cores. Importantly, TSMC fabricates it on its advanced N3B process.
- The GPU tile is responsible for integrated graphics. Moreover, it utilizes TSMC N5P for enhanced graphical prowess.
- The SoC (System on Chip) and I/O tiles manage system functions and connectivity. These, furthermore, TSMC builds on N6.
- A foundational base tile underlies this sophisticated stack. Specifically, Intel manufactures it on its 1227.1 process node, thereby facilitating communication between different chiplets.
Consequently, this multi-foundry, multi-node approach offers unparalleled flexibility. Indeed, it allows Intel to pick the best process for each component.

Lion Cove and Skymont: Core Innovation in Arrow Lake
Arrow Lake features brand-new core architectures. Specifically, you’ll find “Lion Cove” Performance-cores (P-cores), which Intel designs for demanding tasks. Conversely, “Skymont” Efficiency-cores (E-cores) handle background processes; furthermore, they also maintain power efficiency. Therefore, this hybrid approach dynamically allocates workloads, thereby ensuring optimal performance and battery life.
One notable change in Arrow Lake is the removal of simultaneous multithreading (SMT). Indeed, also known as Hyper-Threading, Intel removed it from its P-cores. Although this decision is surprising to some, it reflects Intel’s focus on maximizing single-core performance. Moreover, it simplifies core management. Furthermore, Arrow Lake exclusively supports DDR5 memory; consequently, it ushers in new CUDIMM and CSODIMM standards. These, importantly, Clock Unbuffered DIMM and Clock Small Outline DIMM, offer enhanced stability at high speeds.
Integrated Graphics and AI Power in Arrow Lake
Arrow Lake is not just about CPU performance; rather, it also brings substantial improvements. These, in fact, are for integrated graphics and AI acceleration. The integrated GPU on desktop variants uses 4 Xe-LPG cores. Moreover, Intel bases these cores on the Alchemist graphics architecture. Consequently, they offer a respectable boost for visual tasks and casual gaming. However, mobile versions are even more potent, since they feature up to 8 slightly modified Xe-LPG+ cores. This, therefore, promises a more robust experience for on-the-go content creation and entertainment.
Beyond graphics, however, this generation introduces a dedicated Neural Processing Unit (NPU). This NPU, furthermore, is capable of 13 TOPS. These, specifically, Trillions of Operations Per Second, are for AI workloads. When combined with CPU and GPU capabilities, therefore, Arrow Lake achieves more. Ultimately, it reaches up to 36 TOPS of INT8 performance. This, consequently, provides a significant boost for local AI processing directly on your device. Crucially, this is vital for emerging AI-powered applications and features.
Arrow Lake’s Performance Landscape and Future Refresh
Performance expectations for Arrow Lake suggest a commendable leap. Specifically, you can anticipate up to a 15% increase in multi-threaded performance. This, therefore, makes it excellent for heavy multitasking. Moreover, it also benefits professional applications. Single-threaded performance sees a more modest 5% increase. However, initial benchmarks indicate something else. Arrow Lake’s gaming performance, for instance, may be comparable, or it could even be slightly lower than the previous generation (e.g., Core i9-14900K). Nevertheless, it is also competitive with AMD Ryzen CPUs.
Despite this, however, the architecture places a strong emphasis on power efficiency. Moreover, Intel claims significantly reduced power consumption. Furthermore, they also claim lower operating temperatures. This, consequently, translates to cooler, quieter systems, especially in laptops. Significantly, Intel has acknowledged “holes to fill on the desktop front” with Arrow Lake. Consequently, Intel plans an “Arrow Lake Refresh” for early 2026. This refresh, however, will offer minor clock speed boosts. Furthermore, it will also improve memory compatibility. And it will, moreover, refine voltage-frequency curves. However, it won’t introduce significant architectural changes, nor will it upgrade the NPU.

Nova Lake: The Future of Intel Arrow Lake Nova Lake’s Vision
Arrow Lake lays a solid foundation. However, Nova Lake is positioned as the true architectural successor. Moreover, it represents the next major leap in the Intel Arrow Lake Nova Lake roadmap. Intel anticipates its launch in late 2026 for desktops. Conversely, laptops will follow in early to mid-2027. Nova Lake is where Intel aims to make its most significant impact. Indeed, Intel CFO David Zinsner has publicly expressed high hopes. Furthermore, Nova Lake should address Arrow Lake’s desktop market shortcomings. Ultimately, it should help Intel regain market leadership.
Intel expects this generation to deliver a profound architectural breakthrough. Therefore, it will set new benchmarks for computing power and efficiency. Moreover, it promises enhancements across the board. This includes, for instance, core design and manufacturing processes. Furthermore, it also covers integrated graphics and platform capabilities.
Revolutionary Core Architectures and Scalability for Nova Lake
Nova Lake will introduce entirely new core architectures. Specifically, you’ll see “Coyote Cove” P-cores, which Intel expects to push performance boundaries. Conversely, “Arctic Wolf” E-cores will offer enhanced efficiency. Furthermore, Nova Lake is rumored to incorporate low-power E-cores (LPE-cores). Moreover, Intel designs them to handle the lightest background tasks. This is done, consequently, with minimal energy consumption, thereby extending battery life even further.
Rumors also suggest a substantial increase in core configurations. Therefore, this promises unprecedented scalability. Flagship desktop models could potentially feature up to 52 cores. Moreover, this is an impressive configuration. Specifically, it comprises 16 P-cores, 32 E-cores, and 4 LPE-cores. Consequently, Intel designs this massive core count to tackle demanding multi-threaded workloads. These, for example, range from professional rendering to complex scientific simulations.
To help visualize this significant jump in core density, here’s a comparison:
| Feature | Arrow Lake (Rumored Max) | Nova Lake (Rumored Flagship) |
|---|---|---|
| P-cores (Lion Cove) | Up to 8 | 16 (Coyote Cove) |
| E-cores (Skymont) | Up to 16 | 32 (Arctic Wolf) |
| LPE-cores | 0 | 4 |
| Total Cores | Up to 24 | Up to 52 |
Manufacturing Mastery and Next-Gen Graphics in Nova Lake
Intel expects Nova Lake to push manufacturing boundaries. Moreover, this will happen by employing a hybrid approach. Furthermore, this approach combines Intel’s internal capabilities with external foundry expertise. The critical CPU tiles will likely leverage Intel’s cutting-edge 18A node. Significantly, this represents a major advancement in transistor technology. For other components, furthermore, Intel expects to utilize external foundries. These, for example, could be like TSMC’s 2nm-class process (N2). Therefore, this ensures best-in-class performance and efficiency. Ultimately, this multi-foundry strategy ensures Intel uses the most advanced processes. Crucially, these are available globally for each chiplet.

The integrated GPU in Nova Lake Intel anticipates as a game-changer. Indeed, Intel expects it to use the Xe3 “Celestial” architecture. Consequently, this promises a significant leap in graphics performance. Furthermore, there are even rumors of a more sophisticated hybrid approach. This, for instance, could potentially use Xe3 for primary graphics rendering. A separate Xe4 architecture might handle display and media operations. Such advancements, therefore, could dramatically reduce the need for discrete GPUs. Moreover, this applies to many systems. Ultimately, it offers robust performance for a wider range of users.
Platform Evolution and Cache Innovations with Nova Lake
A truly next-generation architecture often necessitates a new platform. Consequently, Nova Lake is no exception. Moreover, it will require a new LGA1954 socket. Significantly, this signals a major platform shift. Furthermore, it also allows for greater power delivery. Additionally, it also provides increased bandwidth for future technologies. You can also expect support for faster DDR6 memory standards. These, for example, could potentially hit speeds from DDR5-8000 to DDR5-9600 for current DDR5 compatibility. Therefore, this ensures ample memory bandwidth for demanding applications.
Furthermore, Nova Lake is poised to embrace PCIe 6.0. Consequently, this doubles the bandwidth of PCIe 5.0. Moreover, it unlocks incredible speeds for storage. Additionally, it also benefits future expansion cards. Perhaps one of the most exciting innovations, however, is enhanced cache technology. Specifically, this includes “bLLC” (big Last Line Cache). Moreover, this is Intel’s direct answer to AMD’s successful 3D V-Cache. Ultimately, it aims squarely at boosting gaming performance. Furthermore, it also improves overall system responsiveness.
Nova Lake’s Performance Horizon and Market Reclaim
Performance predictions for Nova Lake paint a picture of substantial gains. For instance, rumors suggest improvements of up to 10% in single-threaded performance. Moreover, there’s an impressive over 60% gain in multi-threaded performance. Furthermore, this is compared to Arrow Lake. Therefore, these figures indicate a processor Intel designed to truly excel. For example, this applies to high-performance computing scenarios.
Intel is reportedly laser-focused on reclaiming desktop dominance with Nova Lake. Furthermore, they aim to close and even surpass the gap with AMD’s Ryzen processors. Moreover, this is especially true in critical segments. These include, for instance, gaming and high-performance computing. Additionally, Intel expects Nova Lake to feature NPUs. Crucially, these will comfortably meet Microsoft Copilot+ local acceleration requirements. Therefore, this embeds powerful AI capabilities seamlessly. Ultimately, it integrates them into your everyday computing experience.
To put the rumored performance gains into perspective, consider this table:
| Metric | Arrow Lake (Baseline) | Nova Lake (Projected Increase vs. Arrow Lake) |
|---|---|---|
| Single-threaded perf. | 100% | Up to +10% |
| Multi-threaded perf. | 100% | Over +60% |
| NPU AI Performance | 13 TOPS | Copilot+ compliant (Likely higher TOPS) |
| Memory Support | DDR5 | DDR6 (and faster DDR5) |
| PCIe Standard | PCIe 5.0 | PCIe 6.0 |
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gYEJLi0DAwg
Charting the Course: The Strategic Impact of Intel Arrow Lake Nova Lake
The journey from Arrow Lake to Nova Lake illustrates Intel’s strategic vision. Moreover, this vision is for the future of computing. Arrow Lake serves as a crucial stepping stone. For example, it has a modular design and initial AI integration. Intel refines packaging technologies and also introduces new core architectures. Consequently, these pave the way for more ambitious designs. Nova Lake, on the other hand, represents the culmination of these efforts. Moreover, it is a truly revolutionary platform. Furthermore, Intel designs it to reclaim performance leadership across the board.
For consumers, this means a future filled with better devices. Consequently, these will be more powerful, more efficient, and more intelligent. Gamers can anticipate processors designed to push frame rates higher. Furthermore, they will also reduce latency with advanced cache technology. Content creators and professionals will benefit from vastly increased core counts. Moreover, they will also gain from multi-threaded performance. Meanwhile, everyone will experience a more responsive operating system. Additionally, it will also feature AI acceleration. Moreover, it will handle complex local AI tasks with ease.

Intense competition continues between Intel and AMD. Moreover, this drives innovation at an incredible pace. The upcoming Intel Arrow Lake Nova Lake processors are a testament to this ongoing technological race. Indeed, these architectures are not just about faster chips. Instead, they’re about shaping the future of digital interaction. Furthermore, they also enable capabilities we can only begin to imagine.
What aspects of Intel’s upcoming Arrow Lake and Nova Lake architectures excite you the most? How do you envision these advancements impacting your daily computing? Share your thoughts in the comments below!